Daehan Lim
Cooki - AI Recipe Community App
📝 Overview
📌 App Introduction: Personalized recipe generation and sharing platform powered by generative AI
🕒 Duration: June 1, 2025 ~ July 4, 2025 (1 month)
📱 Platform: Flutter cross-platform app (iOS, Android)
👥 Team Size: 3 developers
💼 Role: AI recipe generation, recipe editing, review features, reporting system, internationalization, etc.
🛠️ Key Technologies: Flutter Dart Firebase Riverpod MVVM Gemini API Firestore Dio Cloud Functions Google Cloud Translation API
🔗 GitHub: flutter-fantastic-four/cooki-app
🔗 App Store: apps.apple.com/kr/app/cooki/id6747327839
📖 Project Background
- Research shows that 27% of cooking beginners fear cooking from scratch, and 38% lack confidence cooking without recipes, demonstrating the need for accessible, personalized cooking guidance.
- Users struggle to find suitable recipes for quick meals using leftover refrigerator ingredients. Existing recipe apps only provide simple search-based functionality and cannot accommodate individual situations and constraints.
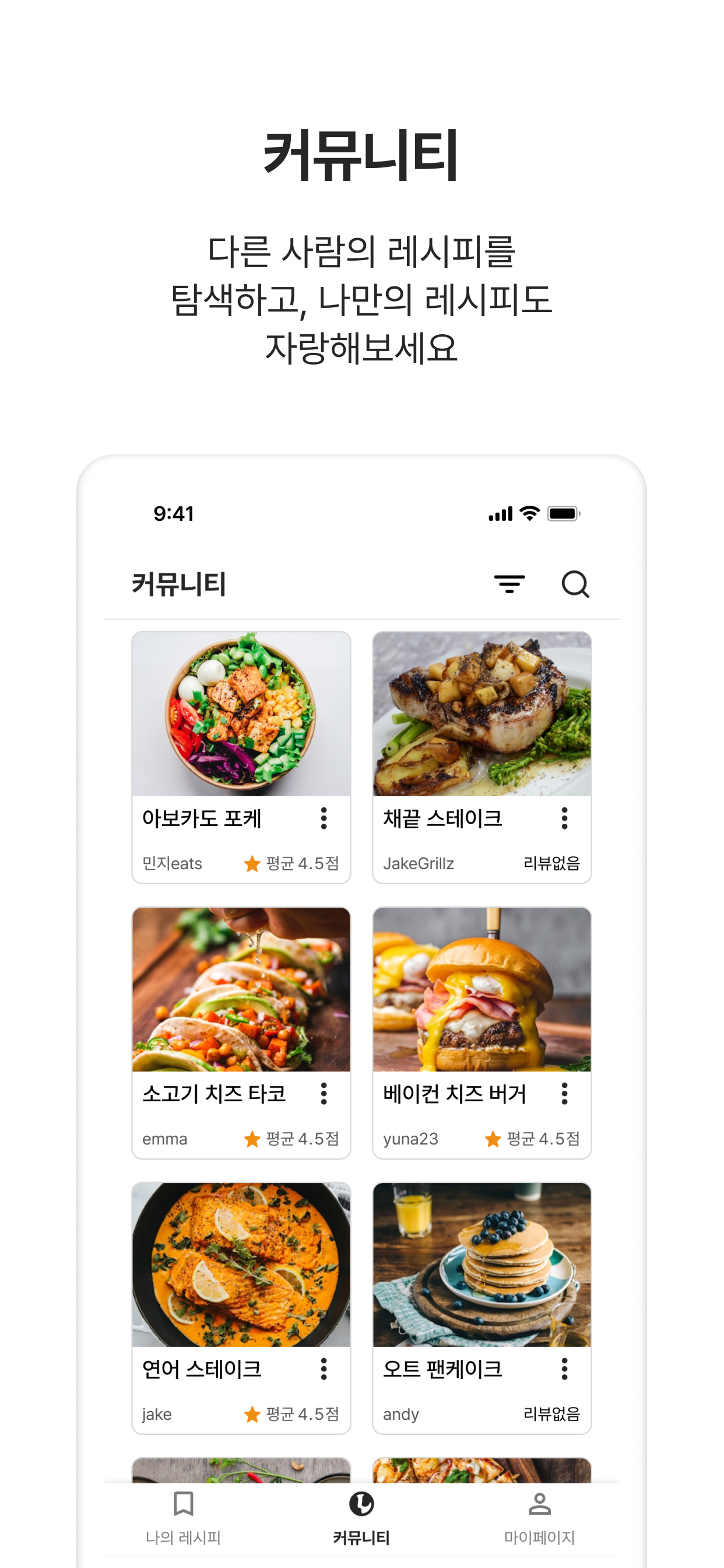
- This led to identifying the need for an integrated platform that leverages generative AI to create real-time personalized recipes based on users’ available ingredients or food photos, while enabling community-based experience sharing.
- The project aims to lower cooking barriers and provide cooking solutions optimized for individual circumstances, creating an environment where anyone can easily start and enjoy cooking.
🛠️ Tech Stack
🌟 Key Contributions
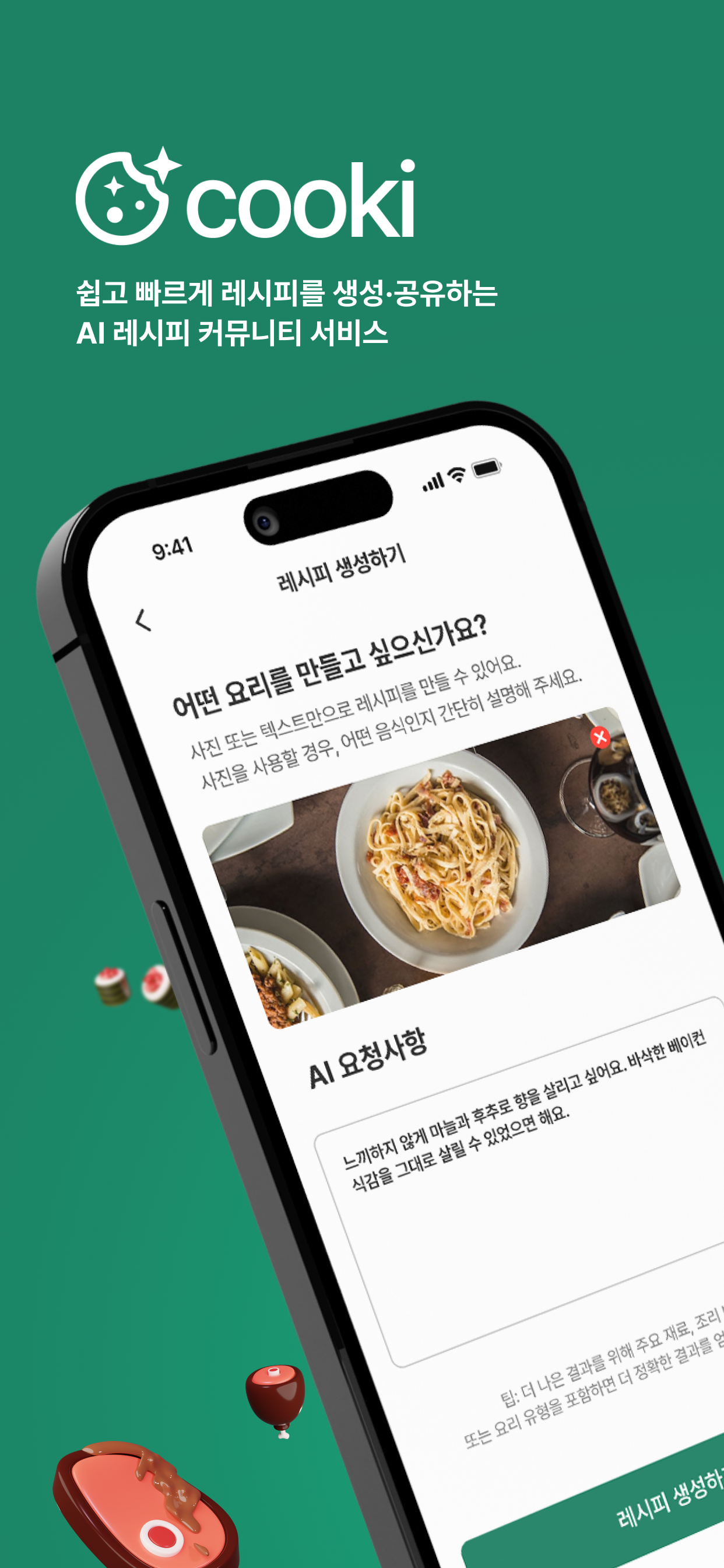
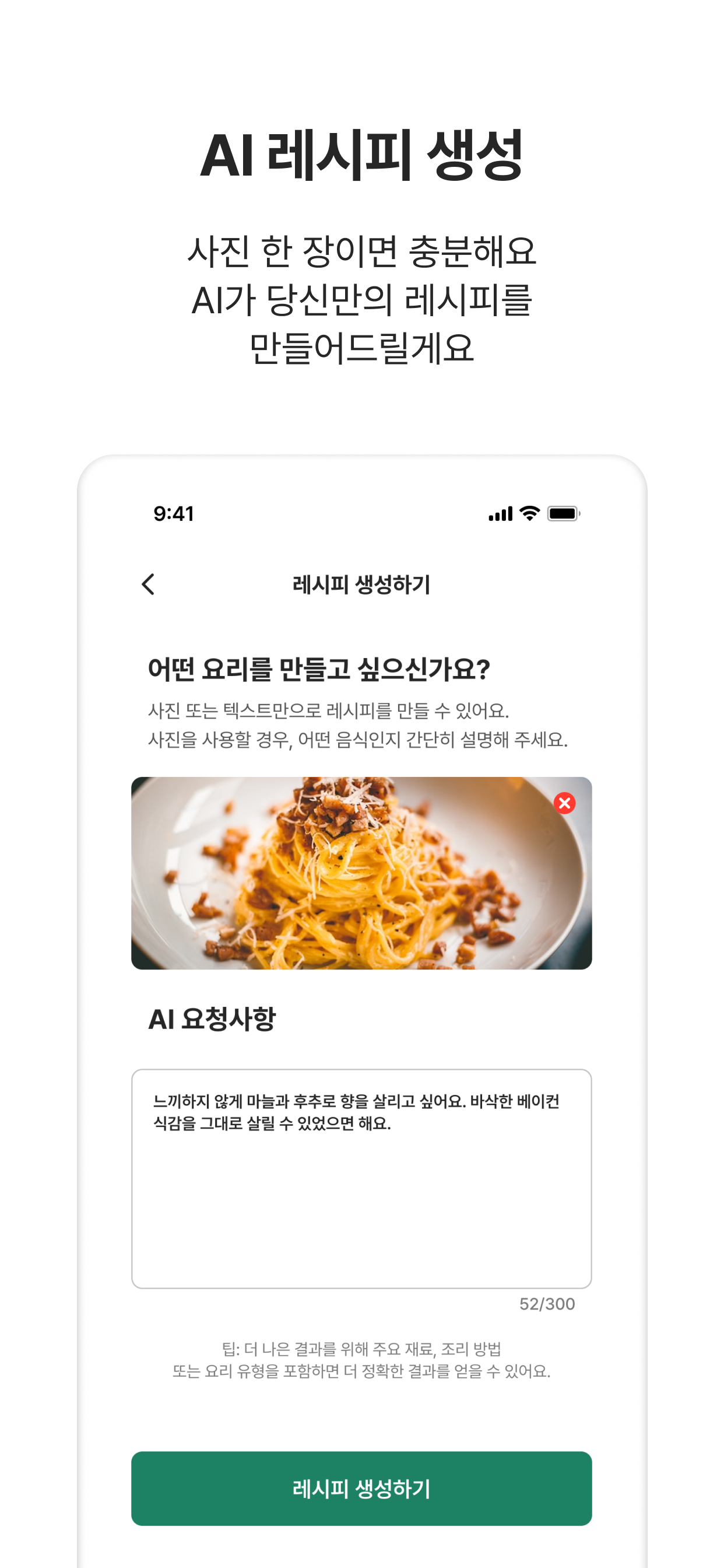
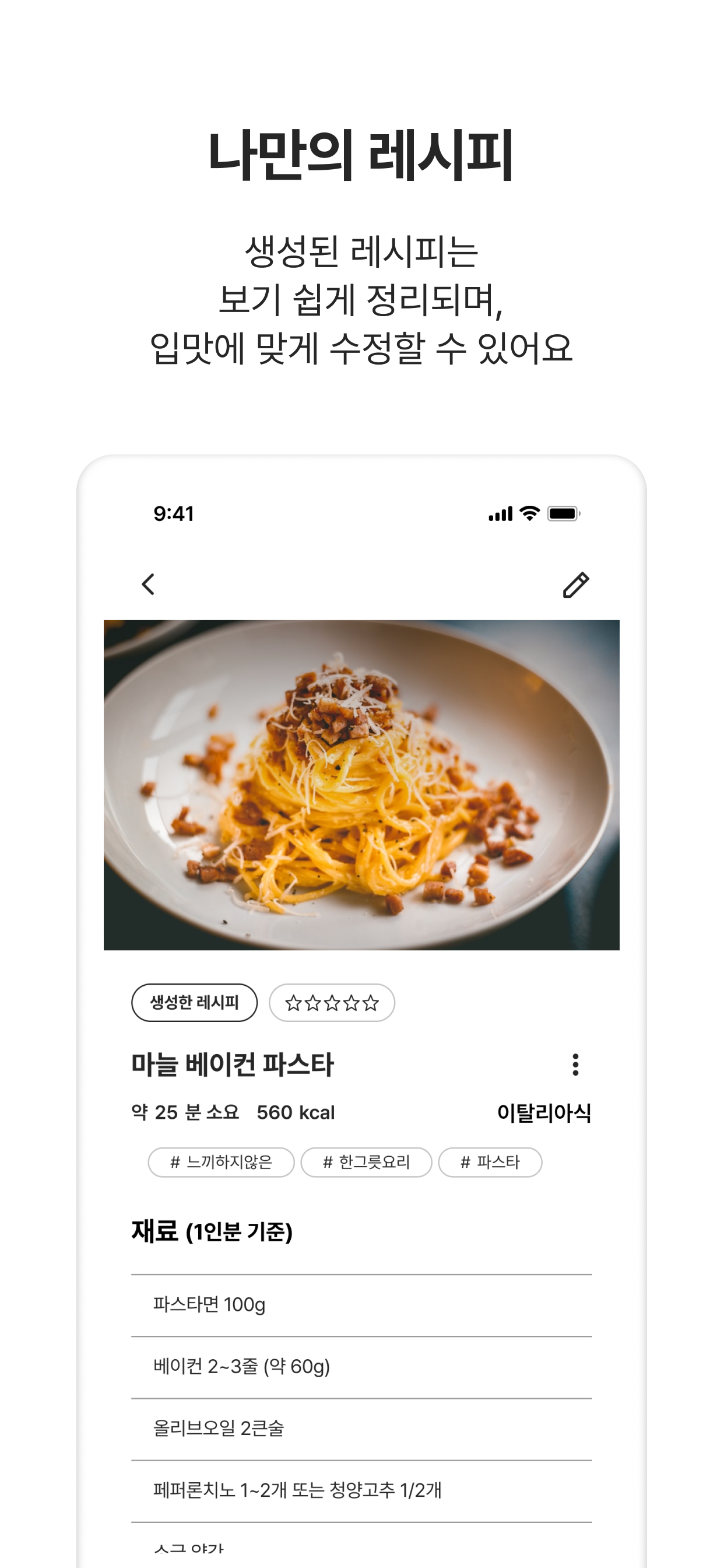
AI Recipe Generation and Management System
- Built
Gemini AI-based multimodal recipe generation system- Integrated
Gemini 2.0-flashmodel for multimodal recipe generation from text input and image recognition - Implemented custom prompt engineering using
Few-shottechniques with user preferences (spiciness level, child-friendly options, etc.) - Developed multilingual prompt configuration and fallback JSON system for non-food images to ensure system stability
- Maintained consistent recipe quality through strict enforcement of category, ingredient, and cooking time specifications
- Created token counting and cost monitoring utility to track input/output token usage and real-time API costs
- Integrated
- AI input validation and quality improvements
- Built separate input validation system using
Gemini 1.5-flashmodel - Created preprocessing logic to filter out non-recipe inputs, command manipulation attempts, and prompt injection attacks
- Implemented a 2-stage validation system separating input validation from recipe generation, reducing inappropriate recipe generation rate from 85% to 12%
- Built separate input validation system using
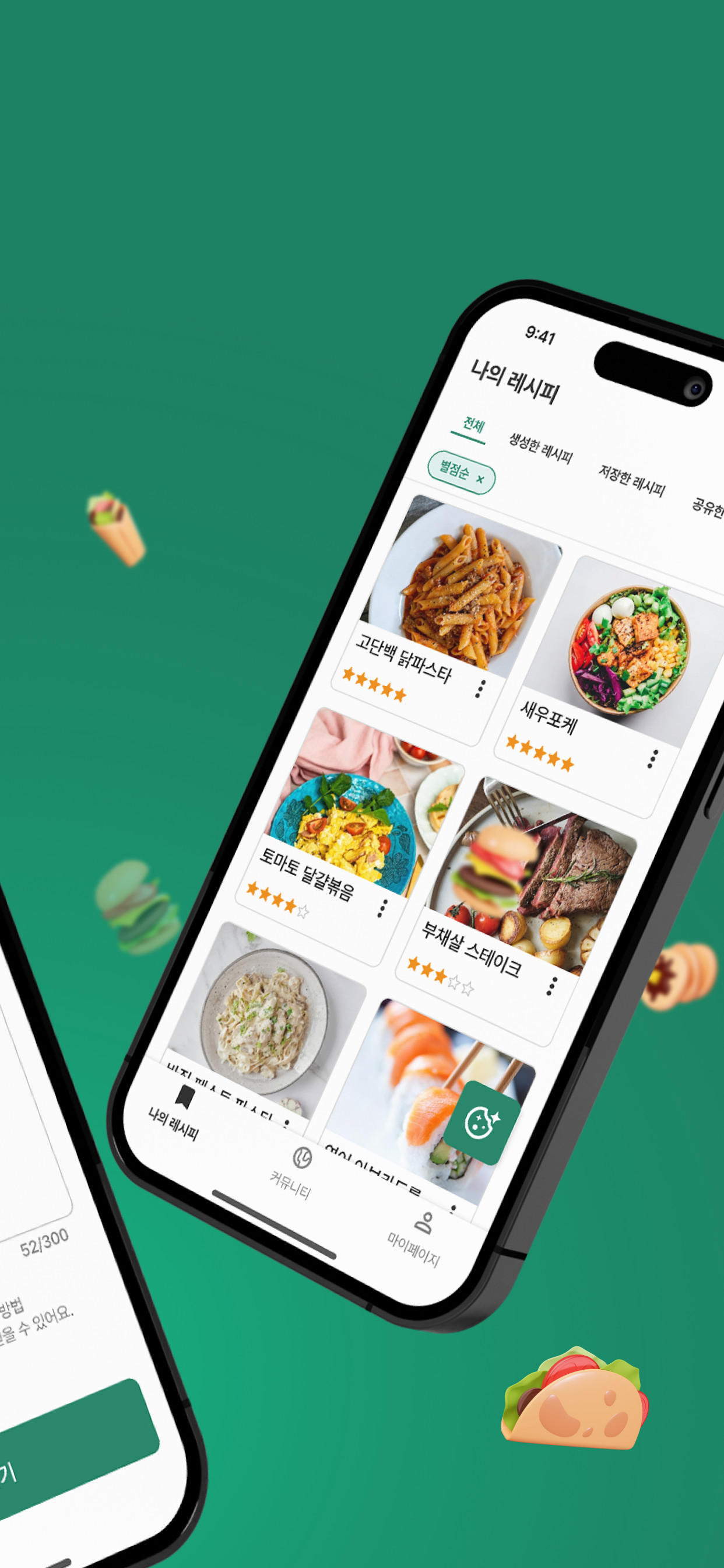
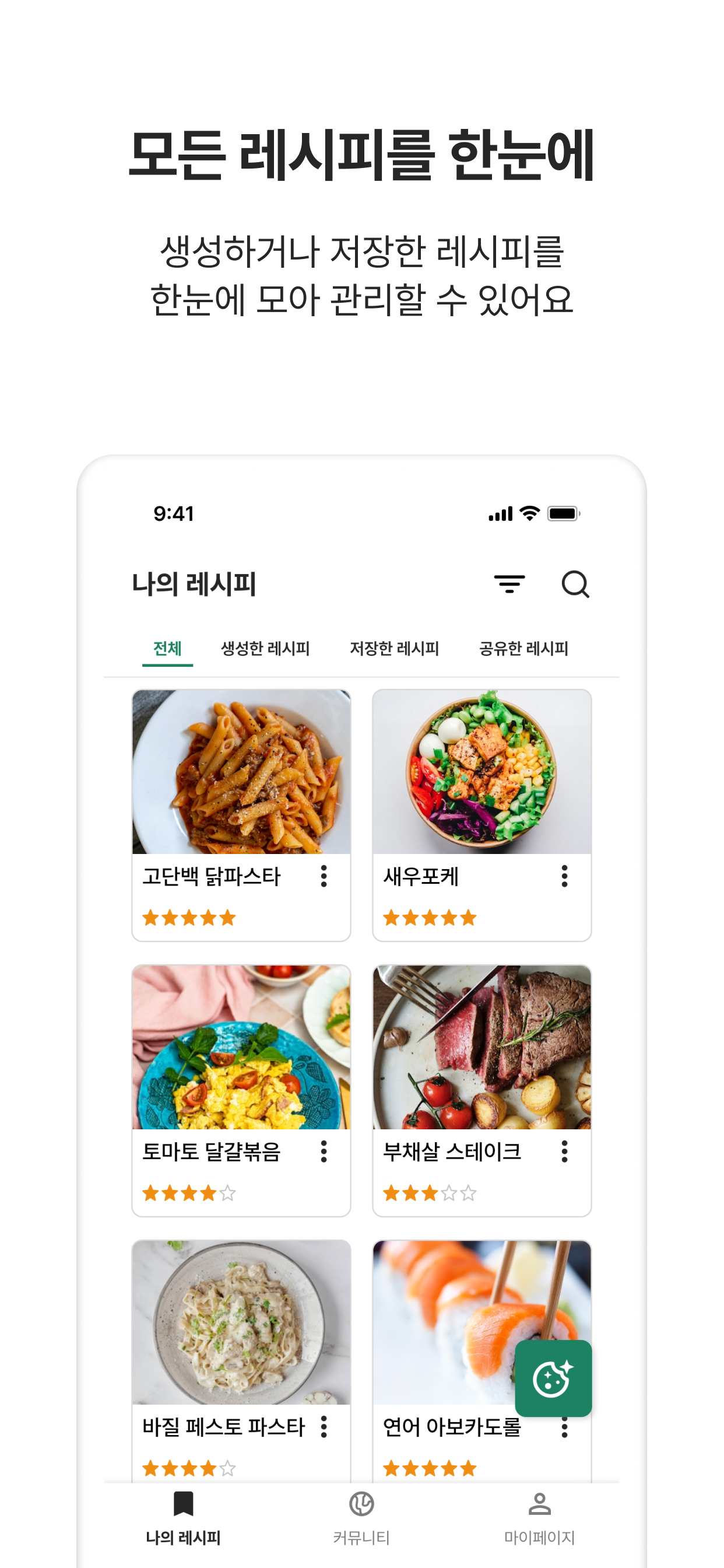
- Recipe storage and management system
- Implemented recipe and image storage functionality through
FirestoreandFirebase Storageintegration - Optimized recipe generation by running AI generation and image upload concurrently, reducing total processing time by 40%
- Implemented recipe editing, deletion and community sharing toggle
- Used
Flutter Image Compressfor image compression and resizing to reduce upload time and optimize storage costs, achieving a 35% reduction in API token usage and improved generation speed
- Implemented recipe and image storage functionality through
Review System and Translation Features
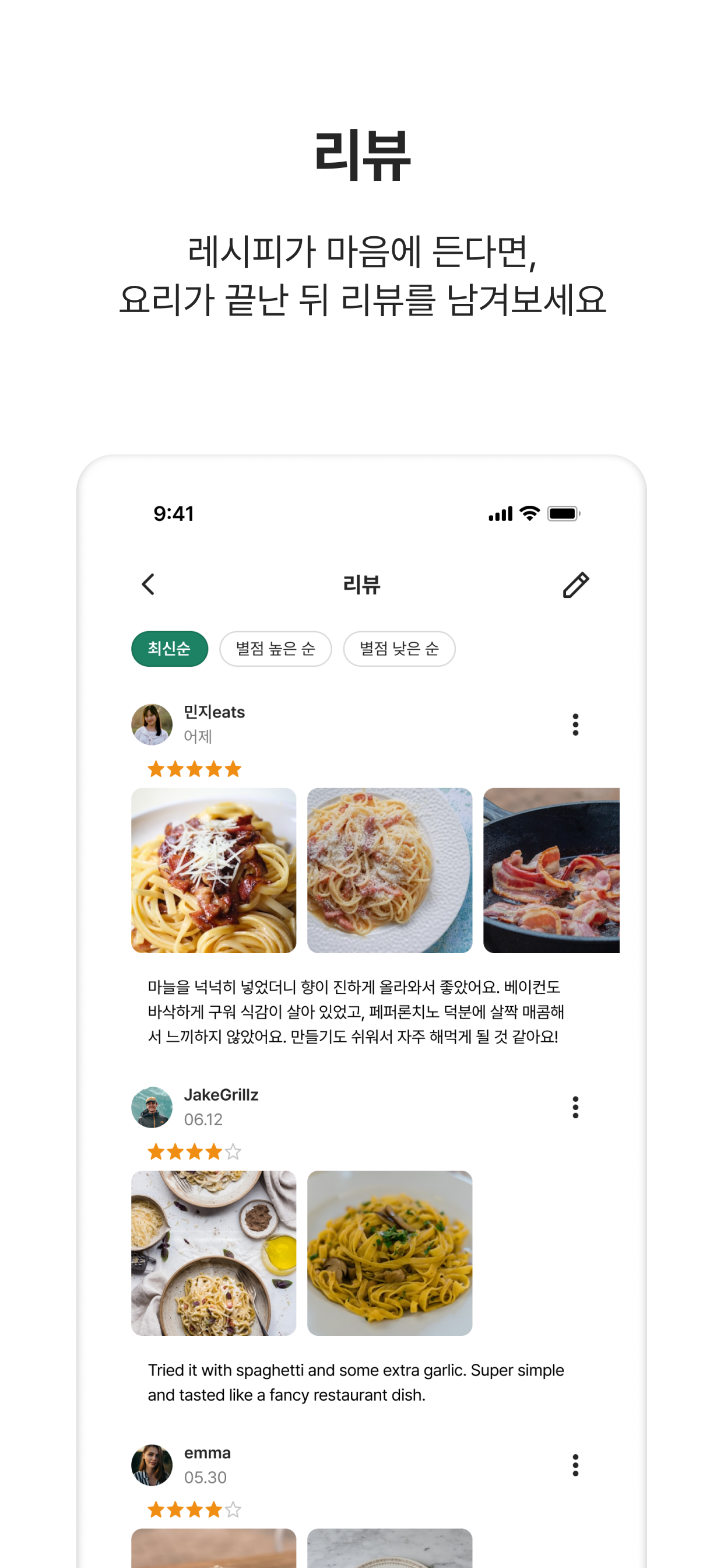
- Review management and interaction features
- Developed review system including star ratings, text, and images (up to 5 photos)
- Implemented review creation, editing, deletion, and content reporting system for inappropriate content
- Enhanced usability with chronological and rating-based sorting options
- Improved review query performance using
Firestoresubcollection structure - Reduced processing time by 40% through individual compression and parallel upload for multiple images
- Provided consistent user experience during editing through a hybrid system that integrates existing server images with newly added local images
- Multilingual review translation system
- Implemented automated review translation functionality with
Google Cloud Translation APIandFirebase Cloud Functions - Introduced automatic language detection during review creation to support seamless communication between multilingual users
- Optimized review submission by processing language detection asynchronously in the background, reducing submission time by approximately 3 seconds
- Implemented automated review translation functionality with
Internationalization and Speech Recognition
- Language settings and internationalization system
- Implemented Korean/English multilingual UI using
Flutter l10n - Stored language preferences using
SharedPreferencesand enabled real-time language switching via settings - Enhanced new user experience through automatic device language detection, defaulting to English for unsupported languages
- Implemented Korean/English multilingual UI using
- Speech recognition-based search system
- Added voice input capability to recipe search using
Flutter Speech-to-Textplugin - Improved accessibility with multilingual (Korean/English) speech recognition support
- Developed real-time text conversion during voice input with error handling logic
- Added voice input capability to recipe search using
Recipe External Sharing Feature
- Implemented combined text and image sharing functionality using
Share Pluspackage - Created readable shared content through structured formatting of recipe information
- Enabled easy recipe sharing to various platforms including WhatsApp, email, and memo apps through Android/iOS native sharing sheets
UI/UX Optimization and Performance Improvements
- Built client-side form validation system with real-time validation for essential fields including recipe title, ingredients, and cooking steps
- Enhanced review image viewing experience with image viewer featuring zoom, pan, and swipe navigation
- Reduced repeated loading time and data usage through image caching using
CachedNetworkImage - Improved perceived performance during data loading and enhanced user waiting experience with
Shimmerloading animations - Used PopScope to prevent accidental data loss when users navigate away from editing screens
Architecture and Exception Handling System
- Exception handling and error management
- Prevented app crashes by catching all exceptions from internal layers in
ViewModeltry-catch blocks - Built 2-stage error processing system: exceptions are converted to domain-specific
Enumerror codes, then mapped to internationalized messages in the UI - Completely separated internationalization dependencies from business logic, enabling
ViewModelunit testing environment and proper separation of concerns - Provided appropriate user guidance for various exception scenarios including network errors and file processing failures
- Prevented app crashes by catching all exceptions from internal layers in
- Code quality and maintainability improvements
- Applied
MVVMarchitecture withRepositoryandDataSourcepatterns for clear separation of concerns - Implemented global state management with
Riverpodand feature-specificViewModelsfor predictable state updates - Built a real-time error monitoring system by integrating local logging with
Firebase Crashlytics - Completely separated DTO and Entity layers to minimize impact of database schema changes on business logic
- Applied
🧭 Technical Decision-Making
1. Gemini AI Model Selection and 2-Stage Validation System
-
Requirements
Need to generate high-quality recipes reliably from user text or image input while effectively blocking non-food-related inputs and malicious prompt manipulation attempts -
Decision
Implemented 2-stage validation system separatingGemini 1.5-flashandGemini 2.0-flashmodels by function- Stage 1 Validation:
Gemini 1.5-flashdedicated to input validation, filtering non-recipe inputs, command manipulation, and prompt injection attempts - Stage 2 Generation:
Gemini 2.0-flashhandles actual recipe generation, leveraging latest model performance and stability - JSON Schema Enforcement: Structured response format prevents parsing errors and ensures consistent data quality
- Token Optimization: Simple boolean response in validation stage saves API costs. Complex recipe data requested only in generation stage
- Stage 1 Validation:
// Validation Model Configuration
_validationModel = googleAI.generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-1.5-flash',
generationConfig: GenerationConfig(
responseMimeType: 'application/json',
responseSchema: Schema.object(
properties: {'isValid': Schema.boolean()},
),
),
);
// Generation Model Configuration
_recipeGenerationModel = googleAI.generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-2.0-flash',
generationConfig: GenerationConfig(
responseMimeType: 'application/json',
responseSchema: Schema.object(/* Recipe structure definition */),
),
);
2. Firebase Cloud Functions-based Translation System
-
Requirements
Real-time translation functionality needed, but directly callingGoogle Translation APIfrom client poses security risk of API key exposure -
Decision
Built serverless translation system usingFirebase Cloud Functionsas intermediate layer- Security: Safely manage
Google Cloud Translation APIcredentials on server side - Scalability: Automatic scaling based on usage and cost optimization through serverless architecture
- Language Detection: Separate functions for translation and language detection enable selective calling as needed
- Error Handling: Unified error handling at
Cloud Functionslevel with structured responses to client
- Security: Safely manage
exports.translateText = onCall({ region: "asia-northeast3" }, async (request) => {
try {
const { text, targetLanguage, sourceLanguage } = request.data;
const translationRequest = {
parent: `projects/${projectId}/locations/global`,
contents: [text],
mimeType: 'text/plain',
targetLanguageCode: targetLanguage,
...(sourceLanguage && { sourceLanguageCode: sourceLanguage }),
};
const [response] = await translationClient.translateText(translationRequest);
return {
success: true,
translatedText: response.translations[0].translatedText,
detectedSourceLanguage: response.translations[0].detectedLanguageCode || sourceLanguage
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error('Translation failed: ' + error.message);
}
});
3. Unified Logging and Crash Monitoring Utility
-
Requirements
Collaborative environment requires consistent error handling, and development team needs rapid identification and response to user environment exceptions after production deployment. -
Decision
Developed logging utility withFirebase Crashlyticsintegration- Single Entry Point: Unified logging approach through single
logError()function for all exception handling - Dual Output: Immediate visibility during development through Dart’s
log()function, automatic collection in production viaCrashlytics - Context Information: Structured error information, stack traces, and optional descriptions improve debugging efficiency
- Reusability: Same interface for exception handling and logging throughout the entire project
- Framework-level Exception Capture: Used
runZonedGuardedto detect and log Flutter framework-level exceptions, preventing app crashes
- Single Entry Point: Unified logging approach through single
void logError(
dynamic error,
StackTrace stack, {
String? reason,
bool fatal = false,
}) {
final message = reason != null
? '[EXCEPTION] $reason\n$error'
: '[EXCEPTION] $error';
log(message, stackTrace: stack);
FirebaseCrashlytics.instance.recordError(
error,
stack,
reason: reason,
fatal: fatal,
);
}
// Usage Example
try {
final bytes = await imageDownloadRepository.downloadImage(
recipe.imageUrl!,
);
...
} catch (e, stack) {
logError(e, stack, reason: 'Image download failed');
}
4. Multimodal Prompt Engineering
-
Requirements
Recipe generation must handle various scenarios including text input, image input, or combinations of both, while providing consistent quality results for both Korean and English users -
Decision
Implemented template-based dynamic prompt system with multilingual markdown file structure- Modular Prompts: Separated base templates, text context, and preference sections into independent markdown files for improved maintainability
- Multilingual Support:
assets/prompts/ko/,assets/prompts/en/structure for language-specific prompt management - Placeholder System: Custom
__COOKI_*__placeholders for dynamic runtime configuration - Few-shot Learning: Example recipes included in prompts ensure consistent output format and quality
Future<String> _buildRecipePrompt({
String? textInput,
Set<String>? preferences,
required bool hasImage,
required String textOnlyRecipePromptPath,
required String imageRecipePromptPath,
}) async {
if (hasImage) {
String imagePrompt = await rootBundle.loadString(
'assets/prompts/$imageRecipePromptPath',
);
// Dynamic section configuration
String textContextSection = textInput?.isNotEmpty == true
? await _buildTextContextSection(textInput!)
: '';
String preferencesSection = await _buildPreferencesSection(preferences);
return imagePrompt
.replaceAll(AppConstants.textContextSectionPlaceholder, textContextSection)
.replaceAll(AppConstants.preferencesSectionPlaceholder, preferencesSection);
}
// Text-only prompt handling...
}
🌱 Problem Solving
1. Recipe Generation and Image Upload Parallel Processing Optimization
-
Problem
Initial sequential processing approach required waiting for AI recipe generation completion before starting image upload, resulting in extended user wait times - Solution Process
- Confirmed that recipe generation and image upload are independent tasks with no dependencies
- Using
Future.wait()enables simultaneous execution of both tasks to reduce total processing time
- Solution
- Extracted image upload logic from existing
_saveRecipe()method into separate_uploadImageIfNeeded()method - Implemented parallel execution of AI generation and image upload using
Future.wait() - Processed each task result individually to handle partial failures
- Isolated error handling logic by task for easier debugging and issue tracking
- Extracted image upload logic from existing
// Original Sequential Processing
final generatedRecipe = await _generateRecipe(
imageBytes: compressedImageBytes, // Send Uint8List binary data to AI
textInput: state.textInput,
// ...
);
if (generatedRecipe != null) {
final imageUrl = await _uploadImageToStorage(compressedImageBytes, user.id);
final saved = await _saveRecipe(generatedRecipe, user, imageUrl);
}
// Improved Parallel Processing
final generationTask = _generateRecipe(...);
final imageUploadTask = _uploadImageIfNeeded(...);
final results = await Future.wait([generationTask, imageUploadTask]);
final generated = results[0] as GeneratedRecipe?;
final imageUrl = results[1] as String?;
- Results
Reduced total recipe generation time by 40%, significantly improving user satisfaction when generating recipes from images
2. Review Language Detection Optimization
-
Problem
Language detection API calls during review creation were processed synchronously, requiring users to wait over 3 seconds for review save completion, creating usability issues - Analysis
- Analysis of review creation flow revealed that language detection is not a prerequisite for saving reviews
- Considered user experience priorities to evaluate separating review saving from language detection tasks
- Identified that language detection results are not immediately necessary and only required when using translation features
- Solution
- Modified the system to execute language detection asynchronously in the background after saving the review
- Removed
awaitkeyword so language detection processes on a separate thread without UI blocking - Maintained consistent processing flow by obtaining the
reviewIdfor background language detection - Isolated language detection failures to prevent impact on core review functionality
// Original Synchronous Processing
await saveReview(review);
await detectAndUpdateLanguage(reviewId); // UI blocking
// Improved Asynchronous Processing
final reviewId = await saveReview(review);
detectAndUpdateLanguage(reviewId); // Background execution without await
- Results Reduced review creation time by approximately 3 seconds, while maintaining translation accuracy and providing instant review saving
3. Image Optimization to Reduce API Costs and Improve Performance
-
Problem
High-resolution smartphone images sent directly toGemini AIincreased tile count, raising API token usage and costs. Large file sizes caused slower uploads and delayed recipe generation - Analysis
- Confirmed tile-based billing: Higher resolution → More tiles → Increased token usage and costs
- Analyzed file size impact: Larger files slow down uploads
- Evaluated quality vs performance tradeoffs: Tested quality and speed across different resizing and compression levels
- Solution
- Resized images to
maxWidth: 768, maxHeight: 768during picking to reduce tile count - Applied
Flutter Image Compresswith 85% JPEG quality, reducing file size while maintaining acceptable image quality
- Resized images to
- Results
Achieved 35% reduction in API token usage, faster upload times, and improved recipe generation speed
4. Filename Collision in Parallel Image Uploads
- Problem: HTTP 400 errors in
Firebase Storagewhen uploading multiple images simultaneously, especially with 3+ images - Investigation: Checked
Firebase Storagerules, quotas, and network connectivity → All normal - Root Cause Analysis: Filename generation using
DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpochcreated identical values during parallel processing, with collision potential in both compression and upload processes - Solution: Changed filename generation logic from
millisecondsSinceEpoch→microsecondsSinceEpochfor 1000x higher precision - Results: Completely eliminated collision errors and enabled stable parallel image uploads